A Customer Success story.
AUTOMATED BUSINESS GLOSSARY
Background
The data landscape is changing so rapidly that without a consistent Enterprise Business Glossary, business users find themselves challenged to deal with a large repository of data dictionary or volumes of technical metadata with no practical method to understand what it all means.
Meanwhile, the Data Governance Office, tasked to create an enterprise glossary, is burdened with the collection of Business Terms and then building consensus regarding nomenclature; “what they are called,” “what they mean,” “how they are related,” “who uses it,” etc.
The Challenge
The great challenge is that business users lack comprehensive documentation related to what they already know. Much of this information exists within the minds of individuals gathered over years of experience. The only way to attempt capture of this knowledge is to conduct manual interviews to understand Key Business Terms and their usage. This manual exercise is time-consuming and cost-prohibitive.
While the scale is a significant issue, the lack of subject matter knowledge within the data organization is also a challenge when attempting to solve a heretofore unsolved problem. When an operating team uncovers a business term and/or metadata, they may not possess the required knowledge regarding their specific meaning and usage.
Need of the hour is to have an Enterprise Business Glossary?
We all have seen a standard glossary, usually located at the beginning or end of a book, contract, or product manual. A Business Glossary is similar, in the sense it does comprise a listing of terms and their unique definitions, but slightly different, as business glossaries have additional information that brings the semantic context to the information.
-In a business glossary, Business Terms are defined using very specific business language and meanings which is agreed on by stakeholders.
-The business glossary will also have additional information such as business rules, which discuss how it is to be used, transformed, calculated, and related.
Why you need one?
Most organizations have a well-structured Data Dictionary. The Data Dictionary contains the technical description of data e.g., Schemas, Tables, Columns, System Specifications, etc. It normally gives details including; Data item, Data Type, Data Element, Member of, Description, etc., meant for data architects and IT professionals. Business users find it difficult to understand these descriptions of data. Business Glossaries bring standardized and unique meaning and context to data within data dictionaries making data easily understood and accessible by all relevant parties.
Our Approach: Unearthing your unstructured data
A machine-assisted approach to discovering key business terms, their meaning, and the relationships that exist to other business terms, along with likely contexts under which they are used, will be the “aha!” moment for any data-driven organization.
Building Business Glossary thru automation
The conventional (manual) method of creating a business glossary often leads to inconsistent definitions, irrelevant term inclusion and false leads. Data teams can easily get into the weeds and progress can be slow and frustrating for all involved. The most obvious solution to shortening the project cycle and ending this frustration is automation.
Introducing Metamap from Parabole
The Metadata discovery and analytics tool, powered by Parabole’s training system (TRAIN), can learn any domain and generate domain-specific language models and the knowledge models required to perform analysis on any enterprise documents. This lightweight training system requires no labelled data nor hours of subject matter expert’s time. This significantly reduces the person-hours required to train machine learning models.
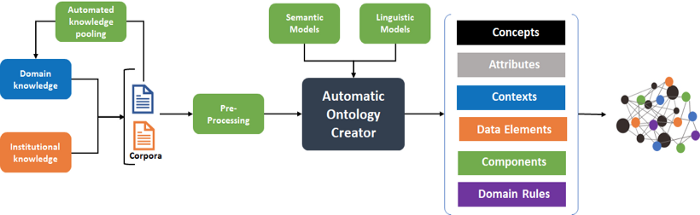
The learned model is then used to analyze unstructured data to discover key business terms, their definitions, relationships with other terms along with their contextual applicability.
Key constituents of Metamap
Discover Business Metadata from Unstructured Data
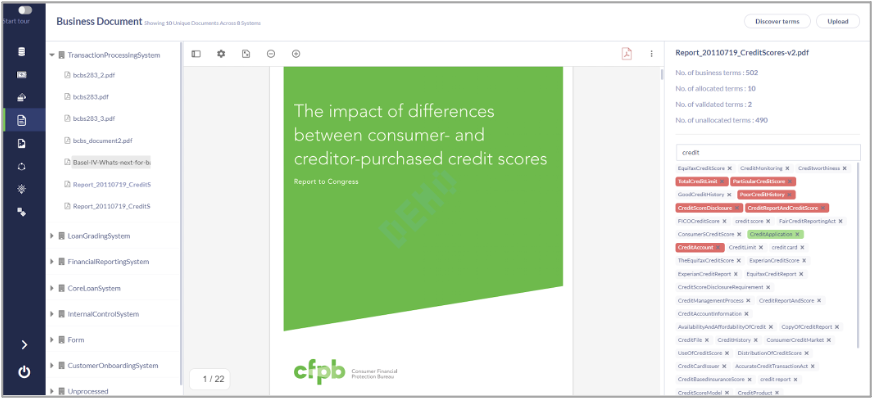
METAMAP discovers a list of Business Terms that are important to Business Users from all relevant enterprise documents. Users can then validate and curate the output based on their project requirements and Business Use Cases.
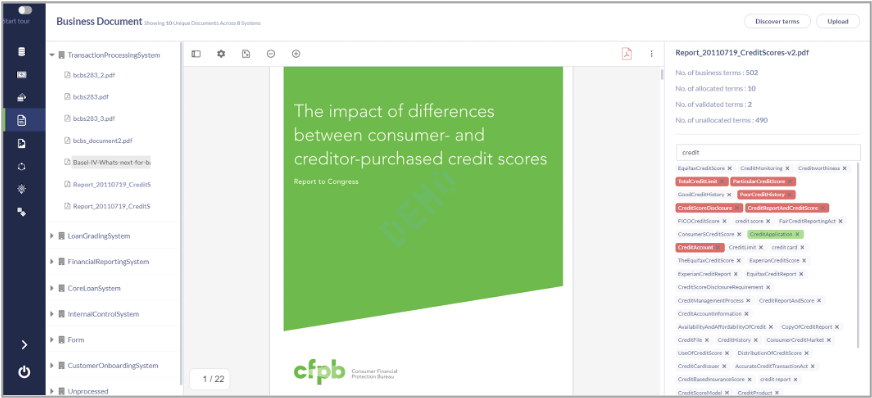
Jumpstart Definition Writing
Developing meaningful definitions requires collaboration and multiple discussions with stakeholders making it a painstakingly difficult process. METAMAP assimilates all relevant definitions present within documents in one place, making it simple and easy for analysts/SME’s to validate and curate definitions prior to acceptance.
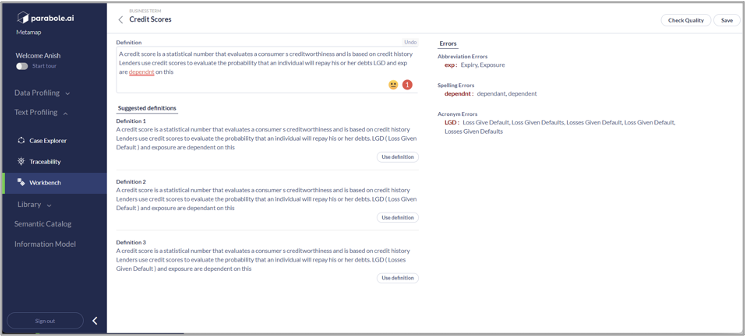
Governing Definition Quality
Having a quality definition is key in the context of accuracy, completeness, consistency, and reliability. METAMAP comprehends the metadata definition quality rules and enforces them on the metadata (e.g., spelling errors/presence of acronym). It also suggests the corrected definition for analyst/SME review.
Connecting the conceptual world with the physical world
A conceptual data model shows how a Business Term connects to other Terms and as well as its linkages to policy, standards, reports, line of business etc. A physical data model has descriptions of table structures including; table name, column name, data type, relationship between tables etc. A metadata catalog view helps both business users and technical users by providing with a blended view of the conceptual world and technical world.
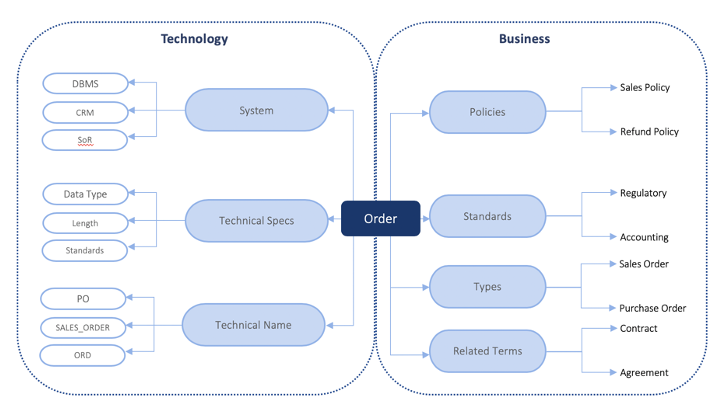
METAMAP discovers the probable relationships between business metadata and their corresponding technical metadata. This helps in modeling the business view of data so that business stakeholders can take ownership of their data, they will no longer need to comprehend physical implementation at the database level.
Key benefits of automating business glossary
An Enterprise Business Glossary provides a single terminology for everyone in the organization so that misunderstandings are minimized. With automated Business Glossary, the Chief Data Office and their Business Partners can derive significant benefits, such as:
1. Single source of truth: All business terms from all reporting tools are automatically mapped and linked to their physical sources within the new glossary.
2. Improved Productivity and Speed of Delivery: It negates the need for face-to-face interviews with Subject Matter Experts Automation expands the capacity manifold by significantly growing coverage and accuracy saving months of manual work.
3. Seamless Collaboration: Easy access and collaboration create an environment that allows for easy interaction between stakeholders with a shared meta-data catalog and business glossary.
4. Re-usable Enterprise Knowledge: Knowledge graph technology enables the creation and access of enterprise knowledge critical for all meta-data discovery and analysis projects.

